Medical tissue samples, critical vaccines, pharmaceuticals and other temperature-sensitive inventory can be compromised if storage conditions are not precisely controlled. For vaccines, even brief exposure to improper temperature can reduce potency, an effect that can’t be reversed. Because these assets often spend significant time in storage before use, cold chain temperature monitoring throughout their entire lifecycle is essential to prevent degradation and ensure safety.
As new drugs are developed, many now include high-value, sensitive ingredients. These medicines often have shorter shelf lives and need to be kept within stricter temperature limits. Biologics, a growing class of medicines, are especially sensitive to temperature changes and need careful, temperature-controlled handling.
To keep products safe and effective, it is important to monitor their temperatures closely at every stage from manufacturing and distribution to storage to end use. Most pharmaceutical products must be maintained between 2 °C – 8 °C.
Anyone handling cold medical products must understand the principles of cold chain temperature monitoring and follow proper protocols to ensure they remain safe, effective and compliant with regulatory standards.
What is the cold chain?
A cold chain is a temperature-controlled supply chain designed to preserve and maintain the quality and efficacy of temperature-sensitive products. To maintain product integrity, all links in the chain must remain unbroken.
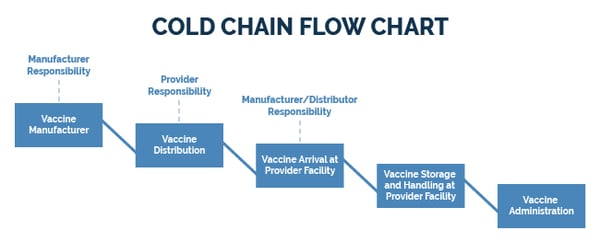
This means that products must be consistently kept within a refrigerated or frozen temperature range from production, through transportation and storage, until administered to a patient.
What happens if the chain breaks?
If the temperature goes out of range, even for a short period, the quality, effectiveness and safety of temperature-sensitive products can suffer. Exposure to improper conditions can reduce potency or cause contamination posing a danger to patients who rely on these medications. Pharmaceutical products that have been improperly stored often must be discarded, leading to potential losses and supply shortages.
The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and local immunization programs strongly advise hospitals and clinics to discard any vaccines suspected of temperature compromise. If this occurs while vaccines are in storage, the facility is typically responsible for the loss, costs that can quickly reach thousands of dollars.
Because damaged vaccines and pharmaceuticals cannot be visually identified, the only real way to protect them is to proactively maintain the correct temperature at all times. Vaccine providers must take proactive measures to implement a cold chain temperature monitoring system that ensures vaccines are stored at the proper temperature until administered.
For Vaccines for Children (VFC) providers, it is mandatory to follow CDC and program-specific guidelines and document that vaccines have never fallen outside the recommended temperature range. If a provider fails to show compliance, there are several penalties and enforcement actions including suspension from the program. A cold chain temperature monitoring system can provide the hard data to verify compliance.
What breaks the cold chain?
The cold chain can be broken for a number of reasons:
Equipment failure
Refrigerators and freezers must run constantly at the correct temperatures to prevent damage to valuable products. Mechanical issues, poor calibration, and worn parts can cause malfunctions resulting in unsafe temperature fluctuations. Routine preventive maintenance helps avoid expensive repairs. But what happens if an issue occurs in between scheduled maintenance visits? Immediate detection of equipment faults or breakdowns is critical to protecting medical inventory.
Power failure
Maintaining a constant electrical supply ensures that vaccines and medicines are stored at the optimal temperature. Power outages can interrupt the cold chain, potentially resulting in widespread loss of inventory. Even short outages can cause temperature fluctuations that compromise product integrity. Temperature monitoring systems are key to mitigating this risk.
Human error
Human error is also a leading cause of cold chain failure. Mistakes such as leaving refrigerator doors ajar, failing to record temperatures, or mishandling items during transfers can break the cold chain. Automated monitoring, along with standard operating procedures, can reduce human error.
Remote monitoring systems for cold chain temperature monitoring

Remote monitoring systems represent the most effective monitoring technology for cold chain temperature monitoring as they continuously track critical equipment conditions and verify that products are constantly stored within the correct temperatures. They offer the strongest protection against the leading causes of cold chain failure.
Remote monitoring systems automatically send alerts to designated personnel when they detect equipment malfunctions, power outages or temperature fluctuations. This proactive notification allows staff to respond quickly, preventing costly downtime and ensuring that medical products remain safe and effective.
In addition to remote monitoring, these systems generate detailed data logs and trend reports that help demonstrate regulatory compliance by providing accurate, continuous documentation of conditions throughout the cold chain. Historical data analysis can identify recurring issues and improve long-term reliability.
While remote monitoring systems require a higher initial investment, they offer significant long-term savings when factoring in labor costs of manual recording and the “costs” of financial risk of compromised vaccines and other assets.
What’s the best way to monitor vaccines?
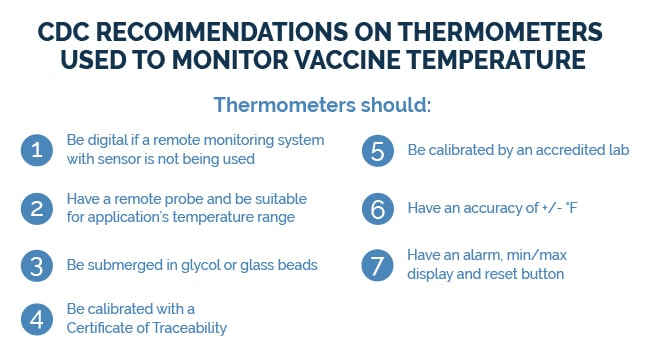
The CDC provides specific guidelines for vaccines (shown below), but similar best practices apply to all medical products, centered on using remote monitoring technology. We recommend monitoring both the refrigerator’s alarm panel and the internal temperature using a temperature sensor/probe. These may be wired or wirelessly connected to an intelligent device called a data logger or remote monitoring system.
To improve measurement accuracy, use a temperature buffer, such as a bottle filled with glycol solution or glass beads, to cushion the sensor against short-term air fluctuations. Without a buffer, sensors record only air temperature, which varies quickly with door openings or fan cycles. Buffered probes provide a more accurate representation of the product temperature of medical assets.
What are validation and compliance requirements for vaccines?
Unregulated temperatures can result in noncompliance with industry standards and government regulations. The CDC, through the VFC Program and in collaboration with state and local health departments, requires strict documentation of temperature compliance for vaccine storage and handling.
Traditionally, facilities used a manual method to record temperatures. A remote monitoring system automates this process by functioning as a data logger that reads and stores temperature data in a secure remote platform.
Personnel can access temperature data in real-time or download reports anytime to prove compliance. Systems allow customizable logging intervals and secure data transmission to the cloud.
Remote monitoring systems also store NIST-traceable calibration certificates, ensuring accuracy and compliance with CDC and VFC requirements. The CDC recommends recalibration every one to two years by an A2LA-accredited lab.
Failure to document can be treated as a storage violation, as regulators cannot confirm that requirements were consistently met. Automated cold chain temperature monitoring eliminates that risk through continuous verification.
How do remote monitoring systems protect medical assets?
Cold medical assets like vaccines, pharmaceuticals and research samples are valuable and sometimes irreplaceable. Their integrity must be maintained from the time of storage until administration or use. Remote monitoring systems, especially those with integrated data logging, protect these assets 24/7 by:
- Continuously recording temperature conditions.
- Providing instant alerts if temperatures move outside acceptable ranges.
- Maintaining an audit trail that verifies proper storage.
A remote monitoring system is a sound investment for cold chain temperature monitoring to secure valuable and temperature-sensitive medical assets and gain peace of mind that vaccines and other biologics are continuously protected under optimal storage conditions.